A Content Delivery Network (CDN) helps optimise the distribution of content by bringing it closer to internet users. But that’s not all: it’s also useful for the speed and security of your website. Here’s everything you need to know about what a CDN is, how it works, and what it’s good for. We’ll also explain how Fasterize is a “next generation” CDN, as well as all the benefits you can get from it!
What is a CDN?
As its name indicates, a Content Delivery Network is a network that distributes content. The servers are organised throughout the world to be able to relay content as fast as possible to internet users, no matter where they are.
In practice, when an internet user requests a piece of content, it is carried from the closest edge server (or relay server; we’ll see the definition a bit later). That way, thanks to a CDN, data have a shorter distance to travel from the server to the browser.
This results in exchanges in the transmission control protocol (TCP) connection and a shorter transport layer security (TLS) handshake, as well as faster loading of the resource. This reduced latency thus very strongly improves the loading speeds of web pages.
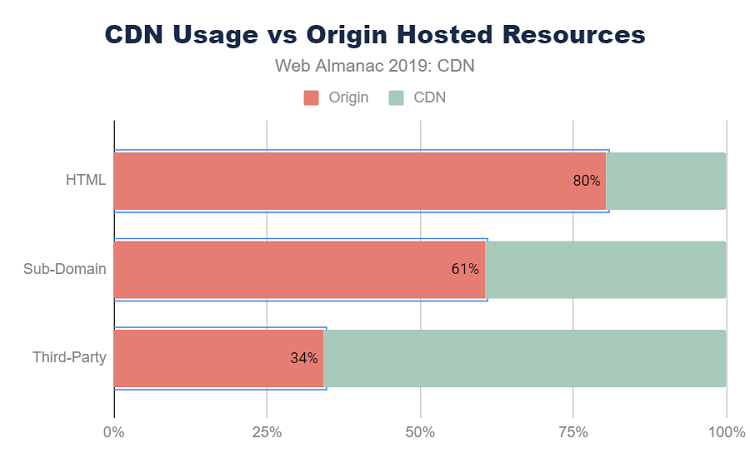
And yet, according to a study conducted by HTTP Archive in 2019, only 20% of websites serve their HTML content through a CDN and only 40% use one to manage their resources. These figures show that CDNs still have a way to go to reach mass deployment, even though they are an essential asset for performance.
How a Content Delivery Network works?
A CDN is a network made up of:
- Points of presence (POP) located worldwide, in populated areas, of course. For countries with a very large territory, there can be numerous POPs. The distribution of POPs varies by provider. Some prefer to cover large areas with small-capacity servers, while others limit the number of POPs but use a large capacity at each one. To choose your CDN, you must find out where the POPs are located to find out if they meet the needs of your traffic.
- Edge servers located at each POP. These are simply proxy caches that function like a web browser cache. They do not generate content; instead, they keep a copy of the content received in their cache. The total number of edge servers located at each POP varies by provider.
When an internet user requests content from a website equipped with a CDN, the request is carried to the closest POP and the edge server then sends the requested data. This pathway is not very simple since it involves carrying web traffic while guaranteeing data security and, at the same time, ensuring continuous availability.
The CDN is far from a simple conveyor belt!
In terms of formats, it can transmit a wide variety of content, including the heaviest, like videos and images. The formats covered can vary from one provider to the next, but the most common are:
- PNG, JPG, SVG, GIF, TIF for images
- FLV, HSL, MP4, MOV, WMV for videos
- MP3, WAV, AIFF, AAC, PCM for audio
And also: CSS, JS, JSON, HTML, PDF, ZIP, TTF, OTF, WOFF, etc.
Without a Content Delivery Network
Without a CDN, your content is served by your origin servers, no matter the location of your users. If your servers are in France but your visitors are in Australia, the data will have to travel all of that distance, which has a significant impact on the overall loading time.
With a Content Delivery Network
With a CDN, your content is served by the POP closest to your visitor. If your origin servers are in France, your users in Australia will receive their content from a POP closer to them and the overall loading time will be reduced considerably.
In short, a CDN brings content closer to users and provides an extra layer of security.
Now, let’s get into the details of its many advantages!
Why to use a Content Delivery Network ?
A CDN for a more stable and reliable website
As we’ve seen, a CDN supplies data from the location closest to a user. But what happens when an edge server is not available?
No problem, one of the other servers in the network takes over. This principle of automatic redundancy guarantees the availability of content under all circumstances.
A CDN for more security
When you use a CDN, your traffic is no longer handled by the origin server and, thus, you limit the risk of distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks. The TLS certificates used by CDNs also encrypt web traffic, securing the data.
A CDN to absorb peak loads
The CDN relieves the origin server of its load and helps absorb peaks in web traffic. It keeps static content in the cache of its edge servers to deliver it as quickly as possible to internet users, even if the origin server is receiving a lot of requests or even reaching its limit. As such, content remains available even during peaks in traffic (note that in addition to our CDN, our engine offers a feature dedicated to managing peak loads: the Traffic Limiter).
A CDN to reduce infrastructure costs
Aa CDN helps reduce your costs for managing infrastructure since it’s the CDN provider who covers those costs. No start-up investments or maintenance costs, and the costs related to the bandwidth of the origin server are also reduced since most content is served from edge servers in the CDN.
A CDN to optimize pages loading speed
This is one of the most important principles we’ve mentioned in this section: with a CDN, content is served from Points Of Presence, bringing content closer to internet users. With a shorter distance to travel, latency is reduced, as is the risk of losing data packets. For this reason, if your site is intended for an international audience, using a CDN is essential! It’s even a prerequisite for improving the performance of your website and the best practice is to combine its strengths with those of an optimisation solution for your front end (which is what our engine does for you, making Fasterize a next-generation CDN).
A CDN to optimize conversions and reduce bounce rates
A next-generation CDN with front end optimisation features gives you a website that’s fast and stable under all circumstances. This is a major advantage when you take into account the impact of loading times on conversion rates, as we discussed in the first section.
In terms of UX, speed is also the top requirement of internet users, especially those using mobile devices: 53% will leave a page if it takes longer than three seconds to load.
With a fast website, in particular, you can limit your bounce rates and boost the engagement of your customers, who will be more likely to complete their purchases.
A final point (one we also mentioned in the introduction): you make work easier for Google, which is able to crawl more pages in less time on your domain, which is an additional advantage for your SEO.
In conclusion, in case you had any doubts left… the role of a CDN can actually be much broader than “simply” bringing content closer to users!
Some CDNs optimise images so that they are lighter on data and adapt to the size of the screen, or they even do that for entire pages so that they load faster (that’s the case with Fasterize).
Malicious traffic is also filtered, offering stronger security, peak loads are absorbed, and infrastructure is more stable while costing less.
Finally, with a CDN, your website gets the benefit of the latest technologies without you needing to adapt your origin server—for example, HTTP/2, or even HTTP/3, TLS 1.3, and IPv6 can be activated via the CDN, even if the origin servers don’t support them yet.
You need a CDN and improve the loading speed of your pages
by optimizing your frontend?
Contact us to learn more about our next generation CDN!